Your cart is currently empty!
Category: Tech Tips

Why are Solar Panels Overstacked?
Over sizing your solar panel array in conjunction with the right solar controller is a strategic move that promises several advantages, especially to deal with harsh winters, frequent cloudy days, or panels that might face dust and age-related efficiency loss. Also, panels are rated using artificial light that’s 1000W/sqm at 25C, scenario that highly differs for real life use.
Here’s why this approach is a savvy choice:
Take, for instance, a Victron 100/20 MPPT controller. By connecting four 250W panels in a 2S2P configuration (~74V Voc & 18.5A Isc) to charge a 24V battery bank, you maintain constant energy input, yielding roughly a fairly constant 480W output. This means during the bulk of daylight hours you’ll produce a constant 20A (max output of MPPT).To make the most of oversizing, it’s crucial to pair your solar panels with an appropriate solar controller that can handle the extra capacity. This ensures optimal energy conversion and management.
Shop Solar
Solar
Our warehouse is full of solar PV panels, rail and mount to suit all kinds of off-grid applications from 4WD, camping & campervans to tiny homes, shacks, agricultural and rural properties. Over 80% of the solar panels we retail are second-life or warehouse seconds. We believe these high-performance products should fulfil their complete functional lifecycle. Panels arrive assessed and we provide a five-year warranty because we are confident in their capabilities.
These are the more sustainable and green option in alignment with our circular economic principles.Availability of specific 2nd life or warehouse seconds panels is unpredictable. Stock levels listed reflect real-time availability and if levels are lower than your requirements, your best option is to choose a different panel. It could be six months, a year, or we may never receive more of a particular panel.
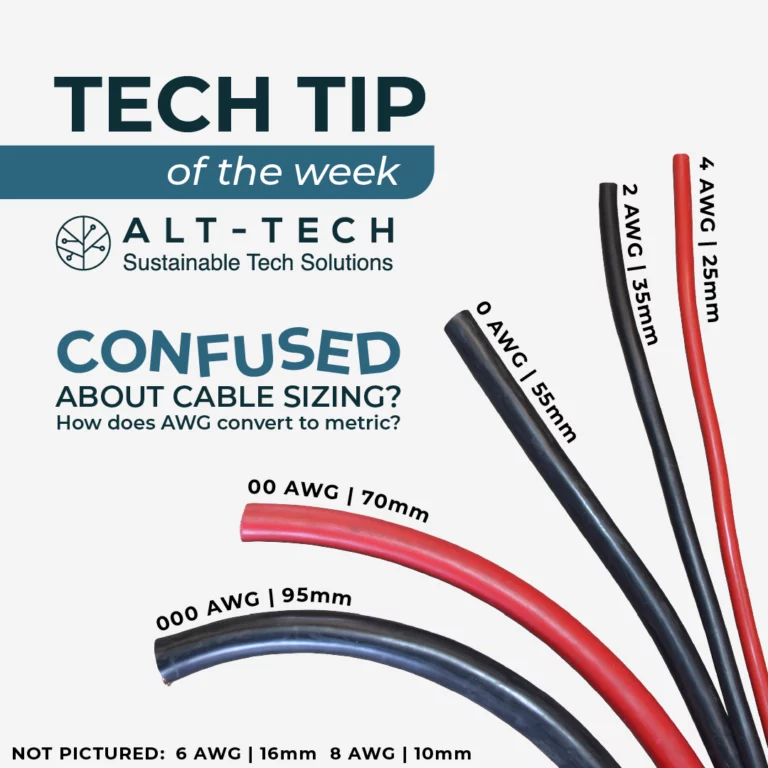
Confused about Cable Sizing?
Confused about cable sizing?
Wondering how AWG converts to metric measurement?The AWG system provides a standardised way to measure wire thickness and is widely used in North America whilst the metric system provides a more straightforward and universally recognised way to measure wire thickness.
In the automotive industry, electrical cables are often labeled using MM standard to denote their size. For instance, you might encounter cables labeled as 2.5mm, 3mm, 4mm, 5mm, or 6mm. However, it’s crucial to note that these measurements don’t directly correspond to the cable’s nominal conductor area in square millimetres (mm²).
Sometimes it can be challenging to get AWG gauged cable to fit in metric lugs. A handy tip is to use electrical tape to compress the wire strands, slide the lug on the end and slowly pull off the tape.Just remember, choosing the right cable size is like finding the perfect pair of shoes – if they don’t fit, you’re in for some uncomfortable dancing, and in our case, a potential electrical meltdown.
Shop Cable

Cable
Our cable wall is stocked with a range of DC, battery, solar and earth cabling for 12v, 24v and 48v off-grid systems so you can purchase all components for your solar power project in one place. Accessories include heat shrink, conduit, lugs and more.

Standard Lugs VS Narrow Palm Lugs
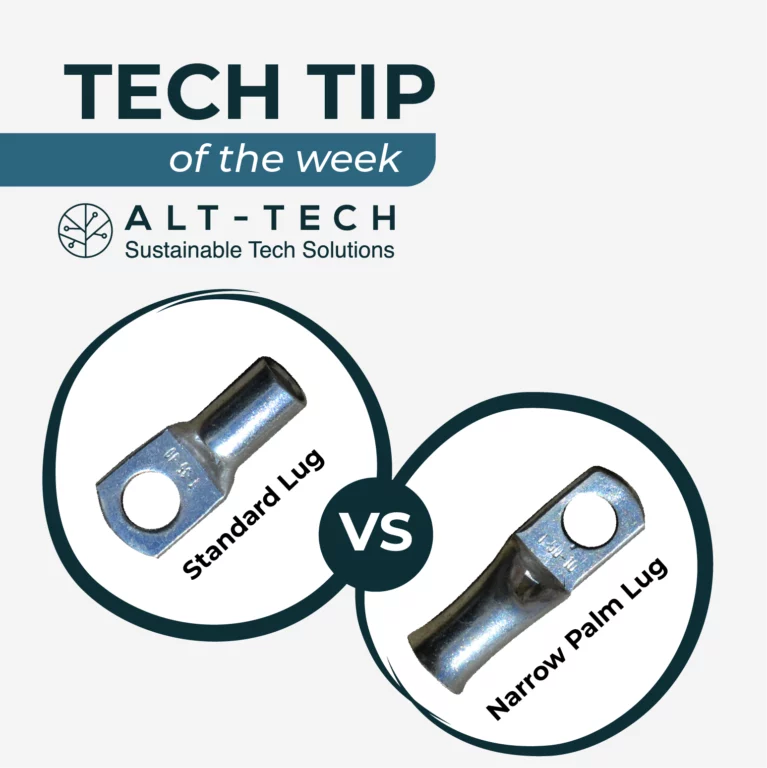



Standard copper lugs are traditional connectors used in electrical and wiring applications; they typically feature a wider palm or contact surface for connecting cables and conductors. Perfect for most applications and high-current applications as they offer more contact surface.
Narrow palm copper lugs are a specialized type of lug connector with a narrower contact surface compared to standard lugs. This design is specifically tailored to certain applications. Awesome for space constrained applications, providing a secure and precise connection maintaining excellent copper conductivity.
When choosing between lugs it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your project. Standard copper lugs offer versatility and high current-carrying capabilities, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
On the other hand, narrow palm copper lugs are ideal when space is limited, ensuring a secure and precise fit.
Which Charge Controller Should You Choose?

Which solar charge controller should you choose?
PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) solar charge controllers are a traditional and simpler technology. They regulate the voltage from the solar panels to the battery by rapidly switching the connection on and off, controlling the battery’s charging rate. Awesome for small-scale solar setups and fixed voltage arrays (panel votlage close to battery). Cost-effective solution but not suitable to charge lithium batteries.
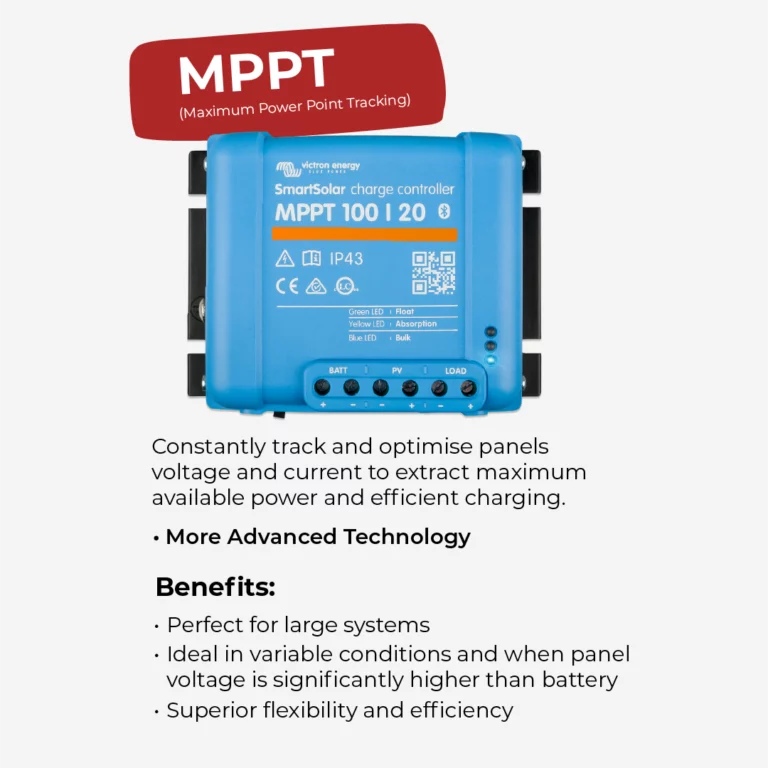
MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) solar charge controllers are more advanced. They constantly track and optimize the solar panel’s voltage and current to extract the maximum available power and efficiently charge the battery. Perfect for larger systems, variable conditions and panel strings with significantly higher than voltage the battery.
The choice between PWM and MPPT solar charge controllers largely depends on the specific requirements of your solar power system. If you have a small, simple setup with fixed voltage solar panels, a PWM controller can provide a cost-effective solution. However, for larger systems with varying conditions and high-voltage panels, an MPPT controller offers superior efficiency and flexibility.
Shop Solar Controllers

Regulators
MPPT and PWM charge controllers for regulating amperage and voltage on solar systems including brands such as Victron bluesolar and smartsolar, Epever and Amptron.

Isolated VS Non-Isolated DC-DC Chargers

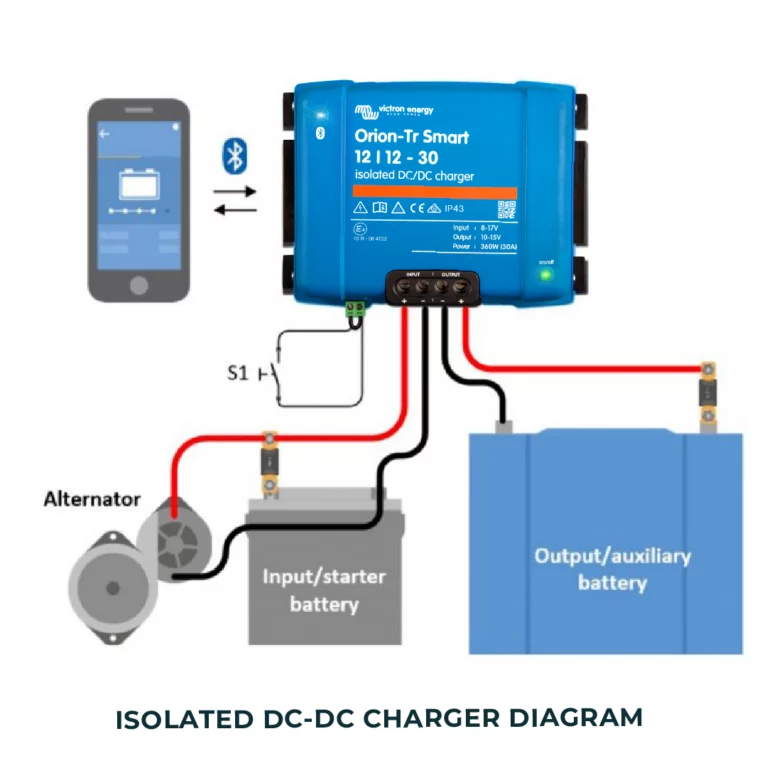
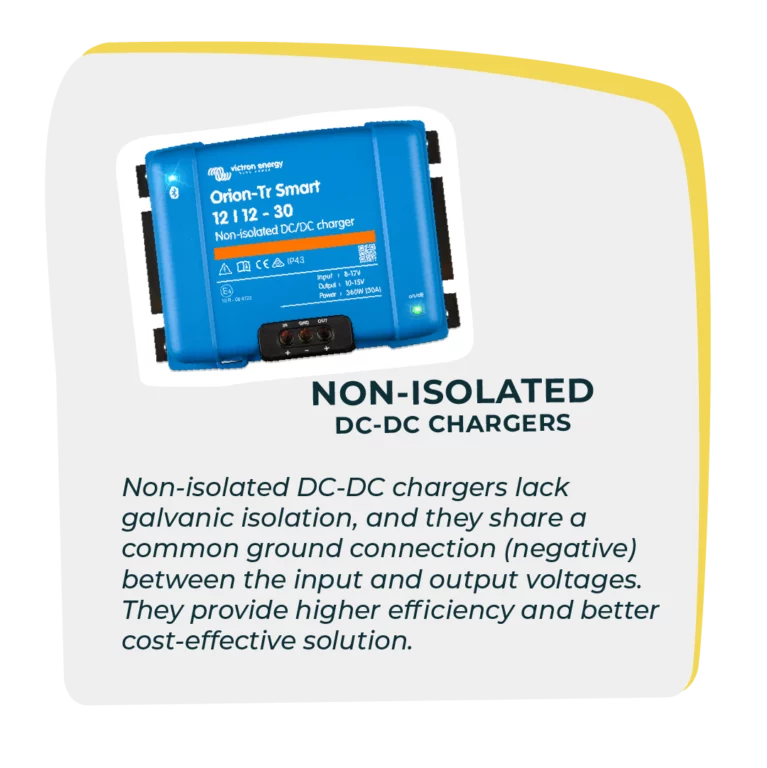
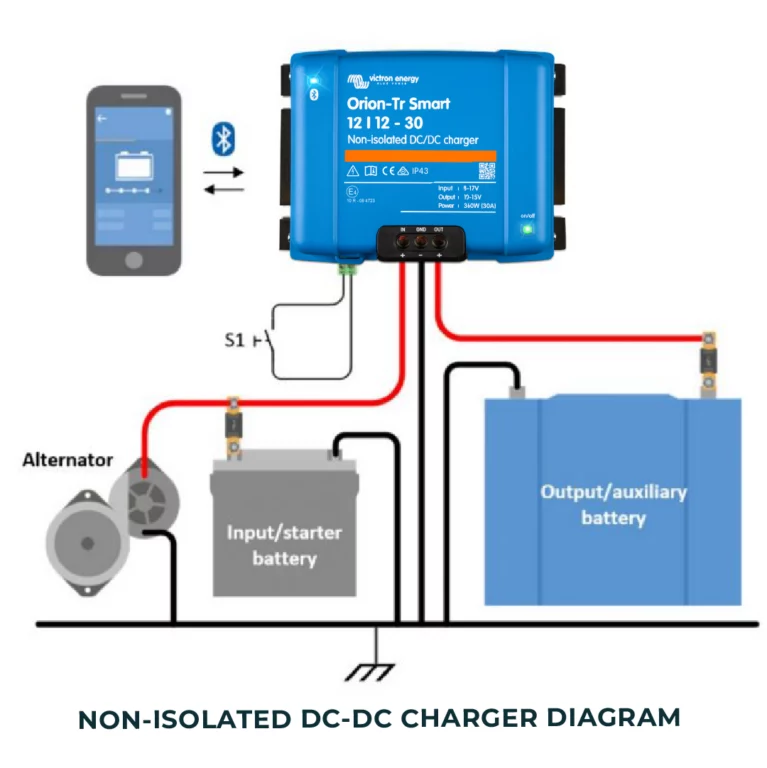
For this weeks Tech Tip we’re comparing isolated and non-isolated chargers, which one meets your needs?
Isolated DC-DC chargers feature galvanic isolation, meaning they electrically and physically separate the input and output circuits. This isolation is typically achieved using a transformer. Effectively reduce noises breaking ground loops, improves electrical safety and shift reference voltage if needed in the application.
Non-isolated DC-DC chargers lack galvanic isolation, and they share a common ground connection (negative) between the input and output voltages. Higher efficiency and are a more cost-effective solution.
How to choose
Choosing between isolated and non-isolated DC-DC chargers depends on your specific project requirements. If safety, ground loop isolation, or reference voltage shifting is critical, isolated chargers are the way to go. On the other hand, if cost savings, space constraints, or energy efficiency are your primary concerns, non-isolated chargers offer a practical solution.Shop DC-DC

DC to DC
Charge and maintain your batteries with DC to DC charging, our range includes convertors and isolated and non-isolated options from brands such as Victron and Enerdrive suitable for 12v, 24v or 48v.
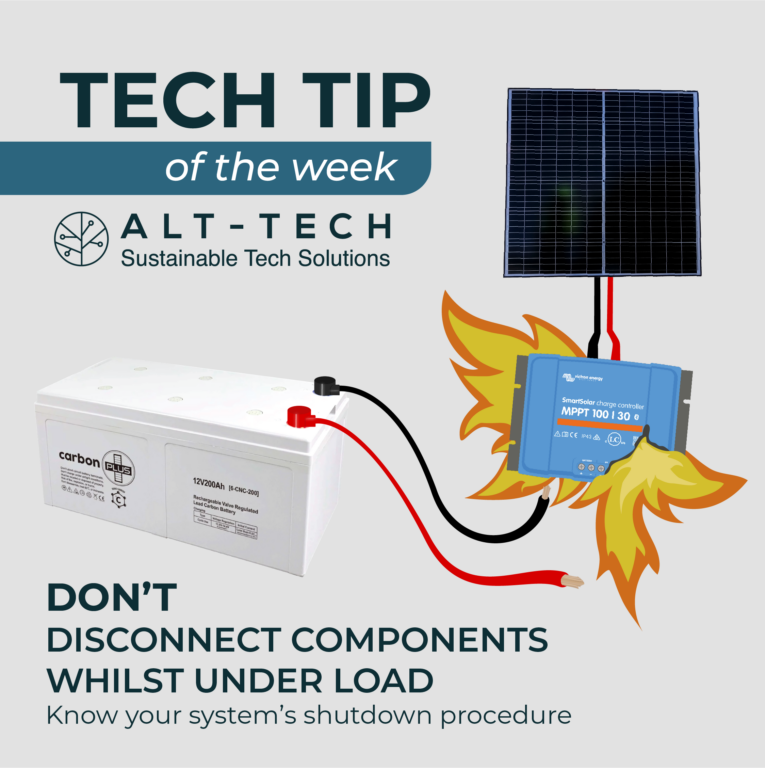
Disconnecting Components
Disconnecting the battery, or any device under load, can cause voltage spikes and fluctuations which may damage the inverter, charge controller, and other sensitive electronics connected to the system, leading to costly repairs, replacements and voided warranty.
To avoid these issues, it’s generally advisable to follow proper shutdown procedures for your off-grid setup, including turning off or disconnecting appliances and systems before disconnecting the battery.
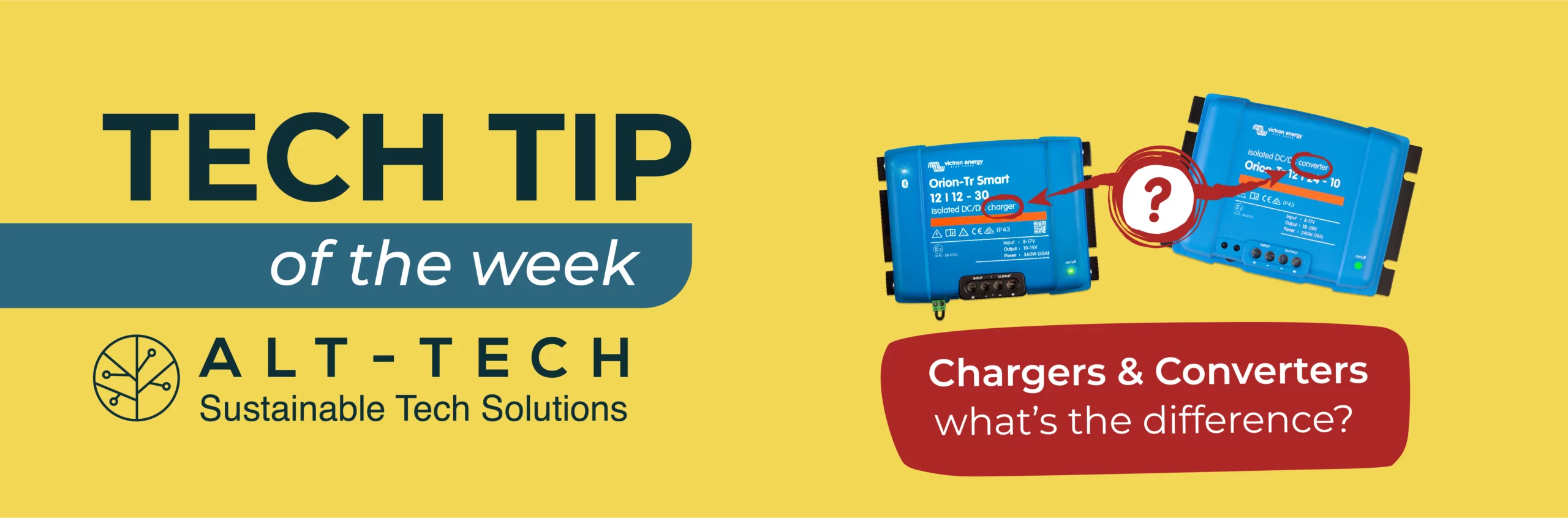
Chargers & Converters: Whats the Difference?



Spot the difference!
Converters and chargers may look alike and might occupy a similar location in your system configuration but they perform different roles.
DC-DC Charger: A dynamic multi-stage charger adjusts voltage as needed, connecting starter and leisure batteries. Efficiently charges the latter from alternator power while your vehicle runs.
DC-DC Converter: Transforms DC input (e.g., 24V to 12V) for stable output at a fixed voltage, perfect for DC devices like fridges or lights. Not for primary charging; mainly for device operation.
Shop DC-DC Chargers and Converters

DC to DC
Charge and maintain your batteries with DC to DC charging, our range includes convertors and isolated and non-isolated options from brands such as Victron and Enerdrive suitable for 12v, 24v or 48v.