Your cart is currently empty!
Tag: Battery Charging

Temperature Compensation
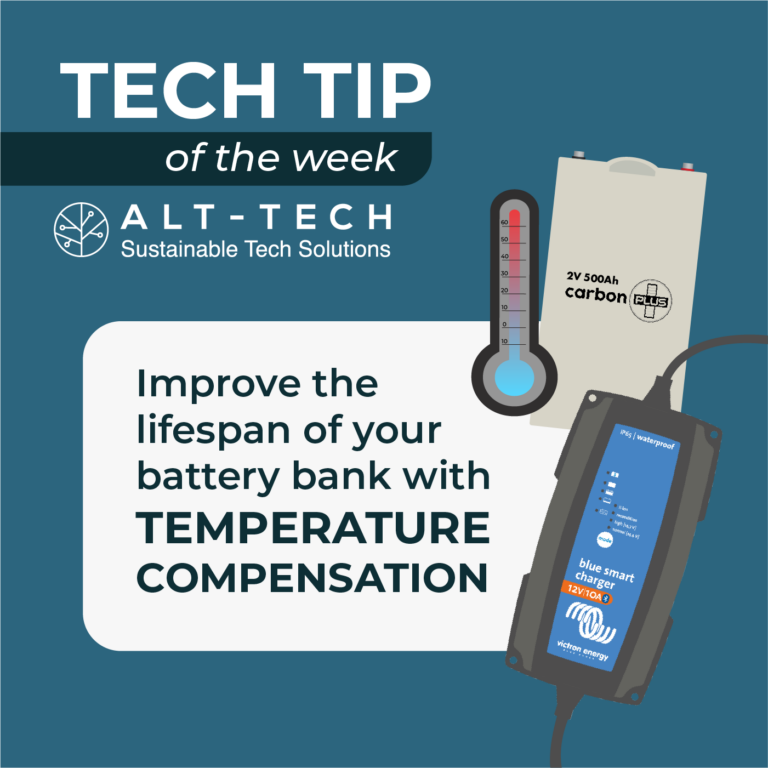

Temperature compensation is a feature of some high quality battery charging devices. It is a setting that allows the charger to adjust the charging voltage of the battery to suit the temperature of the battery. Most battery datasheets specify that the battery charge voltage should be reduced at high temperatures to prolong the battery lifespan.
Correctly setting the temperature compensation of your charger may improve the lifespan of your battery bank. The correct compensation value for your batteries should be available in the battery datasheet or from the battery supplier.
The value you are looking for is something such as -16.20mV/C (Victron Default).

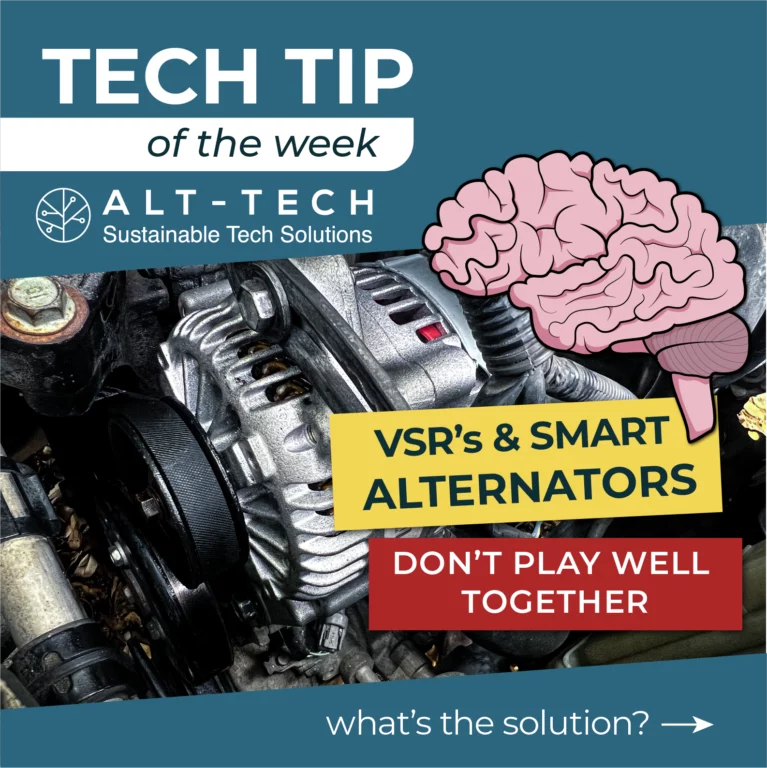
VSR’s & Smart Alternators
Smart alternators (prevalent in most vehicles made after 2006) provide efficient, variable voltage output, reducing emissions and enhancing battery charging. However, this voltage fluctuation doesn’t work well with traditional charging technology like VSR’s (Voltage Sensitive Relay’s).
The VSR’s depend on a constant voltage higher than 13.3V in most cases to be able to charge the auxiliary battery setup. A smart alternator in junction with the ECU of the car will decide when the starter battery is fully charged after cranking and dial the working voltage down after that, causing the VSR flick open and stoping the charging.If you have a smart alternator a DC-DC charger is essential.
These chargers efficiently convert and regulate their working voltage, ensuring your leisure battery receives the right charge, maintaining power on the road.
Shop DC-DC’s

DC to DC
Charge and maintain your batteries with DC to DC charging, our range includes convertors and isolated and non-isolated options from brands such as Victron and Enerdrive suitable for 12v, 24v or 48v.

Isolated VS Non-Isolated DC-DC Chargers
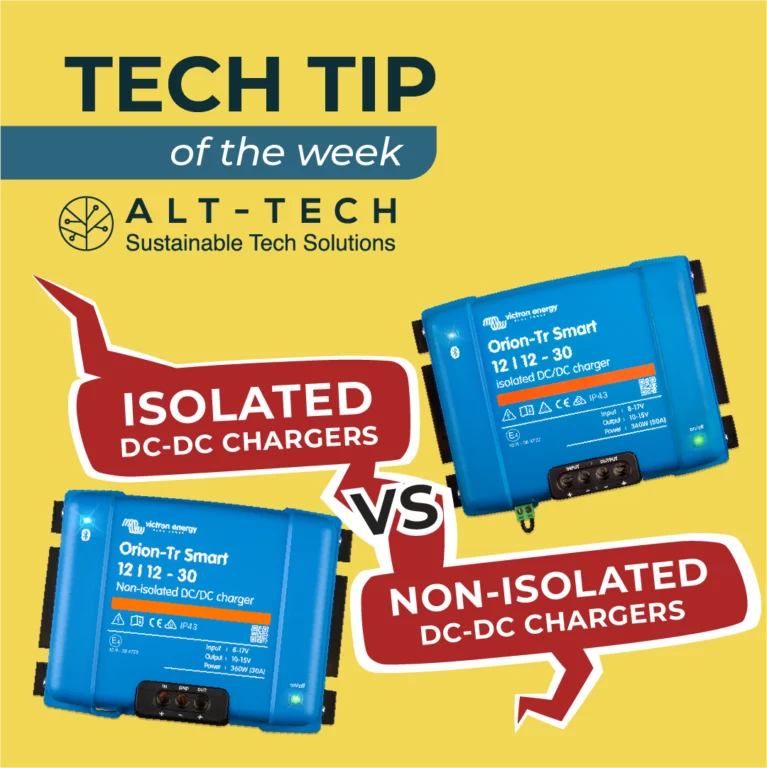

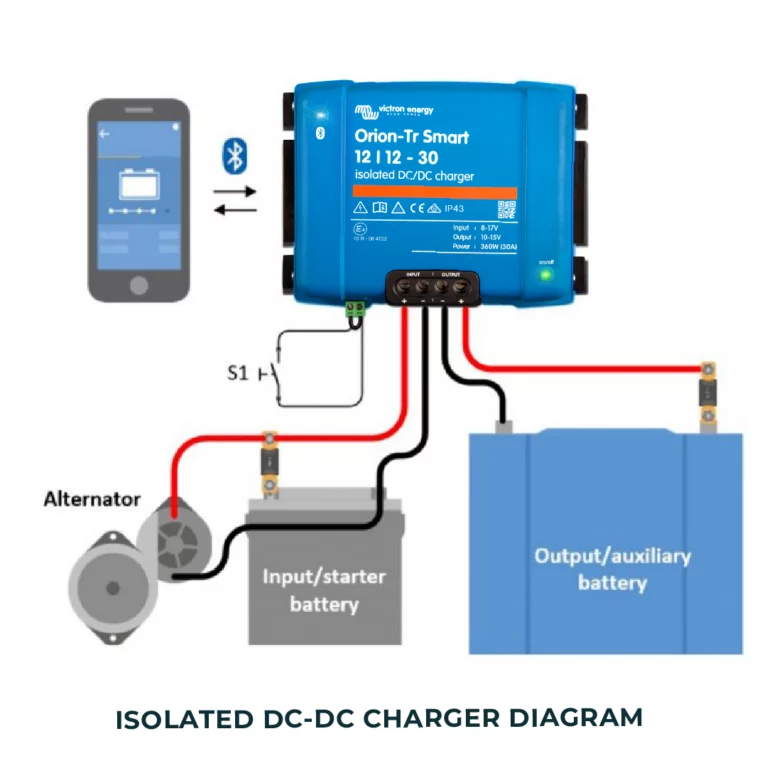
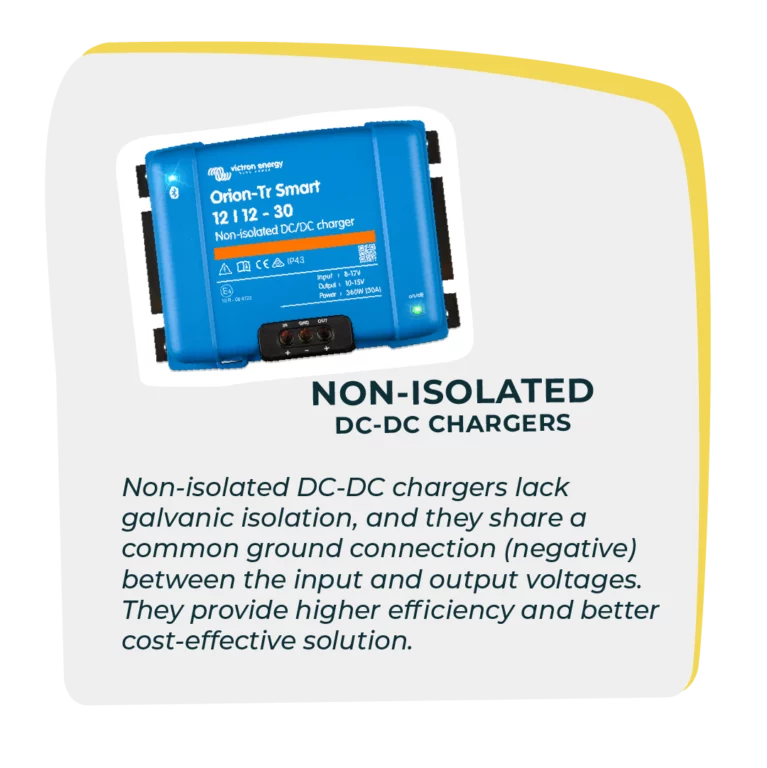
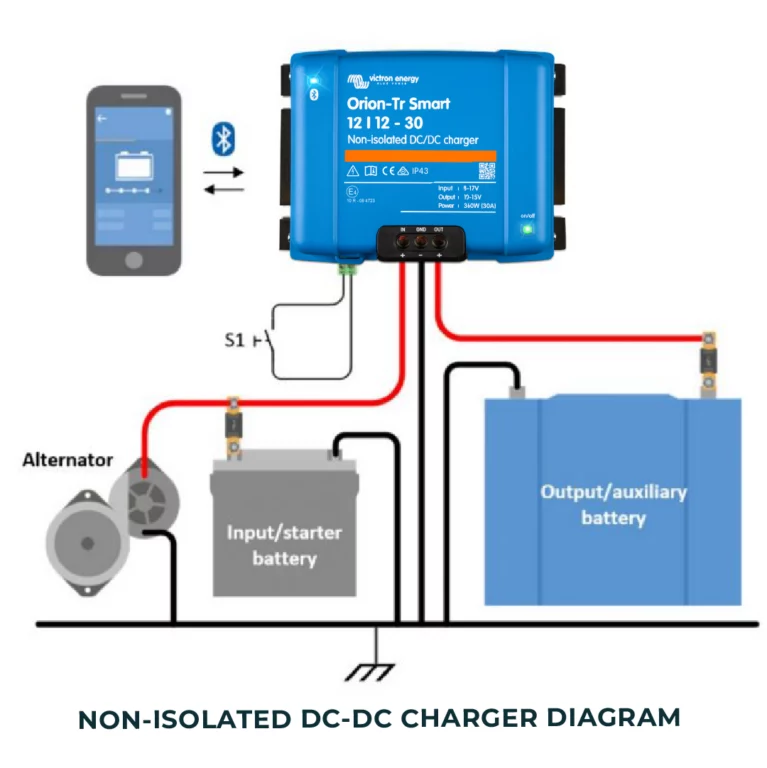
For this weeks Tech Tip we’re comparing isolated and non-isolated chargers, which one meets your needs?
Isolated DC-DC chargers feature galvanic isolation, meaning they electrically and physically separate the input and output circuits. This isolation is typically achieved using a transformer. Effectively reduce noises breaking ground loops, improves electrical safety and shift reference voltage if needed in the application.
Non-isolated DC-DC chargers lack galvanic isolation, and they share a common ground connection (negative) between the input and output voltages. Higher efficiency and are a more cost-effective solution.
How to choose
Choosing between isolated and non-isolated DC-DC chargers depends on your specific project requirements. If safety, ground loop isolation, or reference voltage shifting is critical, isolated chargers are the way to go. On the other hand, if cost savings, space constraints, or energy efficiency are your primary concerns, non-isolated chargers offer a practical solution.Shop DC-DC

DC to DC
Charge and maintain your batteries with DC to DC charging, our range includes convertors and isolated and non-isolated options from brands such as Victron and Enerdrive suitable for 12v, 24v or 48v.
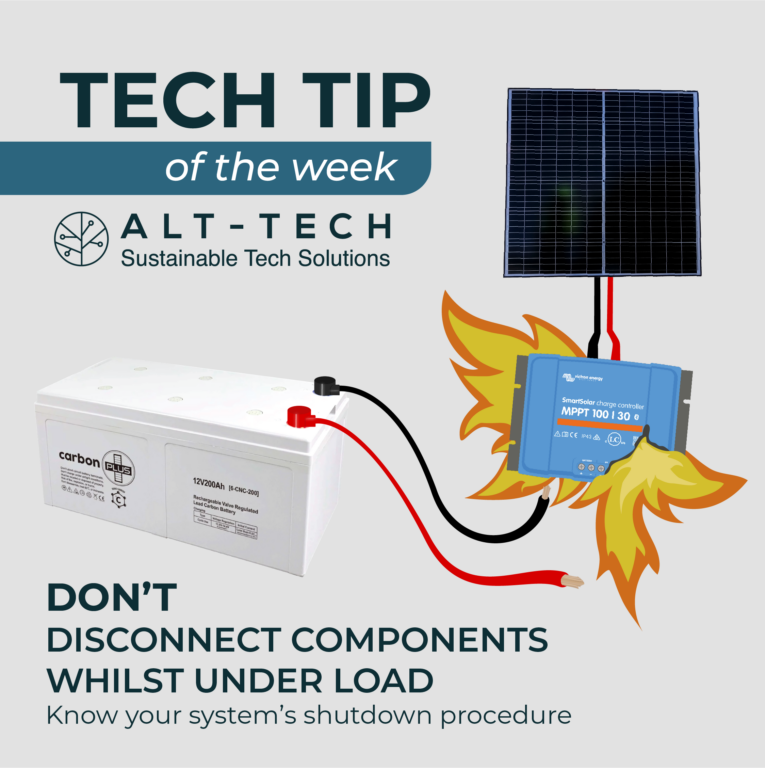
Disconnecting Components
Disconnecting the battery, or any device under load, can cause voltage spikes and fluctuations which may damage the inverter, charge controller, and other sensitive electronics connected to the system, leading to costly repairs, replacements and voided warranty.
To avoid these issues, it’s generally advisable to follow proper shutdown procedures for your off-grid setup, including turning off or disconnecting appliances and systems before disconnecting the battery.
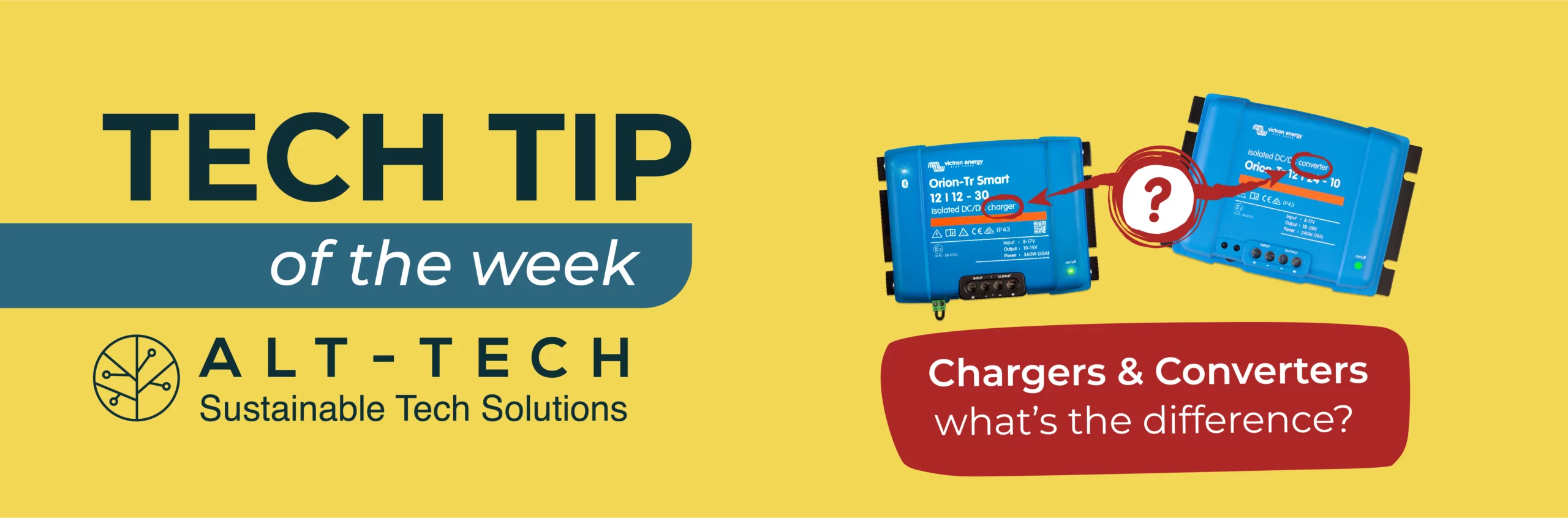
Chargers & Converters: Whats the Difference?



Spot the difference!
Converters and chargers may look alike and might occupy a similar location in your system configuration but they perform different roles.
DC-DC Charger: A dynamic multi-stage charger adjusts voltage as needed, connecting starter and leisure batteries. Efficiently charges the latter from alternator power while your vehicle runs.
DC-DC Converter: Transforms DC input (e.g., 24V to 12V) for stable output at a fixed voltage, perfect for DC devices like fridges or lights. Not for primary charging; mainly for device operation.
Shop DC-DC Chargers and Converters

DC to DC
Charge and maintain your batteries with DC to DC charging, our range includes convertors and isolated and non-isolated options from brands such as Victron and Enerdrive suitable for 12v, 24v or 48v.