Your cart is currently empty!
Fuses: Safeguarding your System Wiring



When calculating the fuse for your system, remember: The fuse’s primary role is to safeguard the wire’s integrity.
They shield against potential fire hazards by breaking the circuit if something goes wrong.
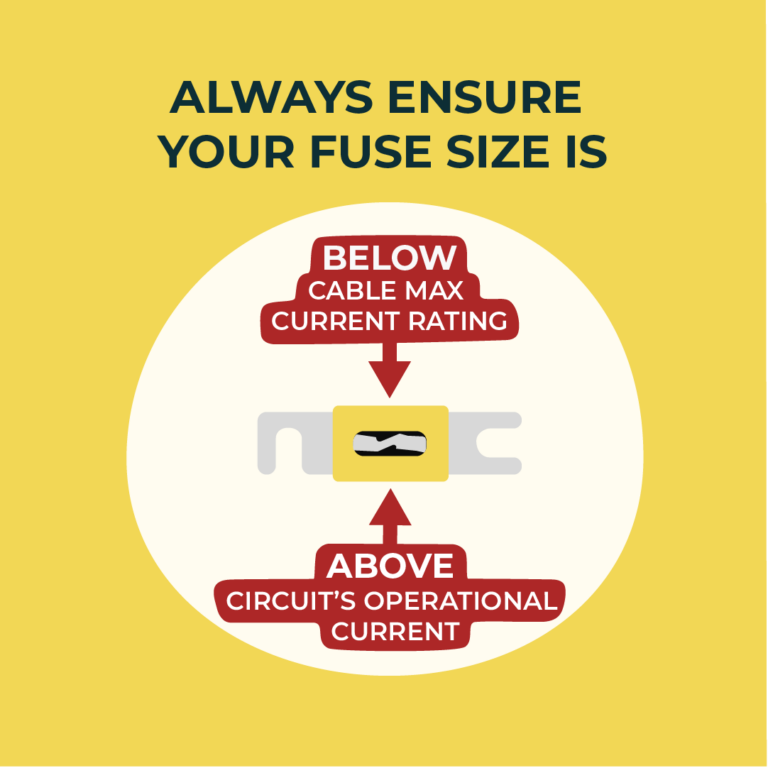
- Ensure your fuse size is above the circuit’s operational current and below the wire’s maximum current rating.
- Prioritize system safety by understanding that a well-sized fuse is your wire’s first line of defense.
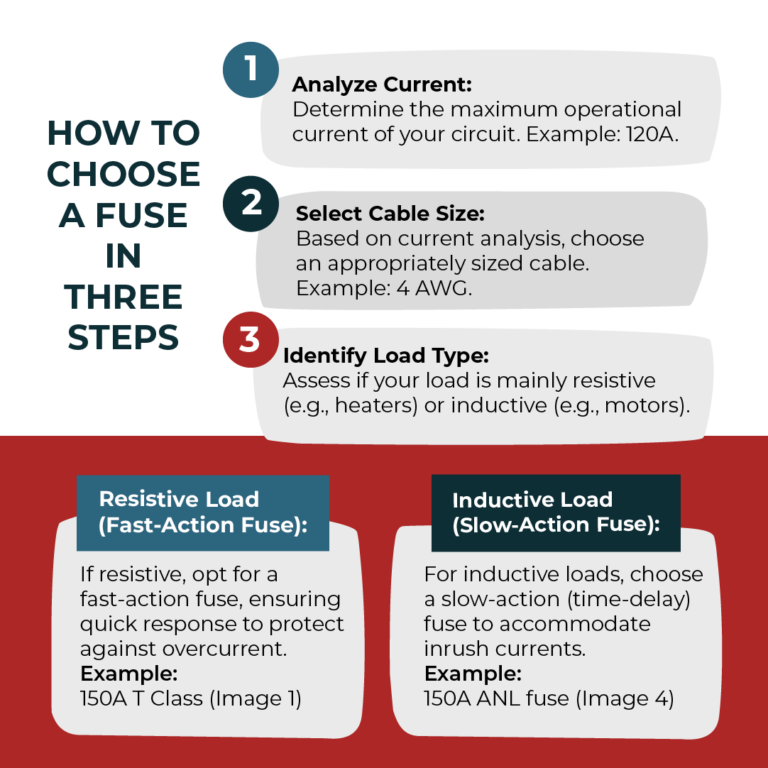
The following three steps will help you determine the best type and size of fuse for your system.
- Analyze Current: Determine the maximum operational current of your circuit. Example: 120A
- Select Cable Size: Based on current analysis, choose an appropriately sized cable. Example: 4 AWG.
- Identify Load Type: Assess if your load is mainly resistive (e.g., heaters) or inductive (e.g., motors).
Resistive Load (Fast-Action Fuse):If resistive, opt for a fast-action fuse, ensuring quick response to protect against overcurrent. Example: 150A fast-blow fuse.
Inductive Load (Slow-Action Fuse):For inductive loads, choose a slow-action (time-delay) fuse to accommodate inrush currents. Example: 150A time-delay fuse.
Check Manufacturer Recommendations when possible! If you need more advice our sales team are always happy to help.
Shop Fusing

Fusing
All your off-grid, DC electrical circuit protection needs are covered with ANL fuses, Blade fuses, FH type fuses and Victron megafuses, plus housing and holders.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.